 |
Salil Gokhale, Harshul Sagar, Rohit Vaish, and Jatin Yadav AAMAS 2025 arXiv The paper develops constant-factor approximation algorithms for one-sided and two-sided Nash social welfare under submodular and subadditive valuations, respectively, and capacity constraints. |
 |
Hadi Hosseini, Andrew McGregor, Justin Payan, Rik Sengupta, Rohit Vaish, and Vignesh Viswanathan Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems Journal paper How to assign a set of numbers to the vertices of a graph to minimize the sum of absolute differences along the edges? |
 |
Umang Bhaskar, A R Sricharan, and Rohit Vaish Information Processing Letters Journal paper / arXiv Using Sperner's lemma to show the existence of a connected and equitable division of a cake. |
 |
Surbhi Rajput, Ashish Chiplunkar, and Rohit Vaish SOSA 2025 arXiv How an online algorithm, that buys or sells stocks based only on current prices, can compete with an offline prophet that knows all prices beforehand. |
 |
Ramsundar Anandanarayanan, Swaprava Nath, and Rohit Vaish Extended Abstract at AAMAS 2024 Fairly allocating homogeneous divisible resources among agents with different consumption rates and arrival and departure times. |
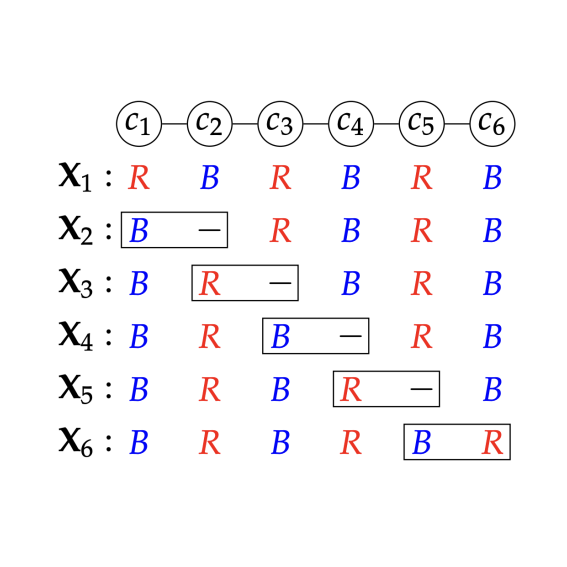 |
Sarfaraz Equbal, Rohit Gurjar, Yatharth Kumar, Swaprava Nath, and Rohit Vaish Extended Abstract at AAMAS 2024 / arXiv How to fairly allocate resources under conflict constraints? |
 |
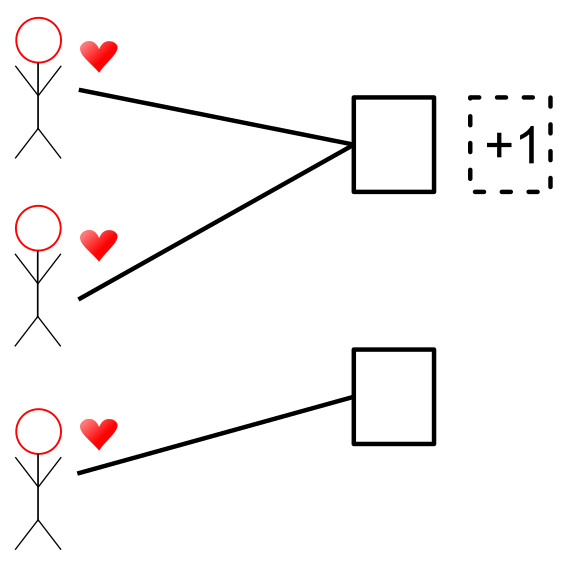
Ayumi Igarashi, Vishwa Prakash, and Rohit Vaish AAAI 2025 arXiv When some resources are pre-assigned, how should the remaining resources be distributed to make the final allocation fair and efficient? |
 |
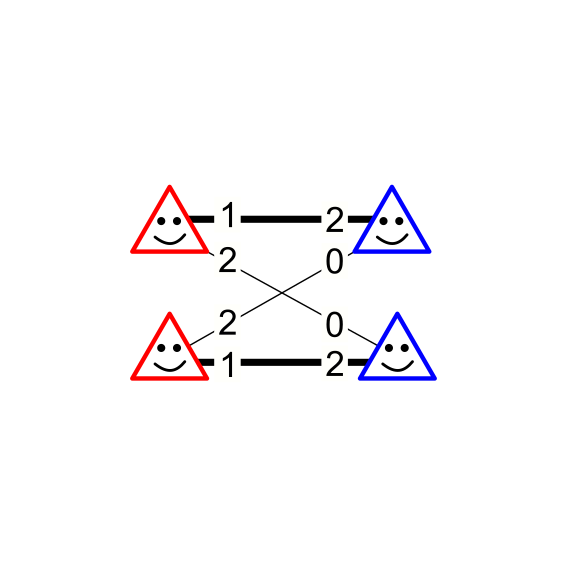
Salil Gokhale, Shivika Narang, Samarth Singla, and Rohit Vaish AAMAS 2024 Conference paper / arXiv In the many-to-one stable matching problem, how can the capacities on the "many" side be modified to achieve desirable outcomes as stable solutions of the modified problem? |
 |
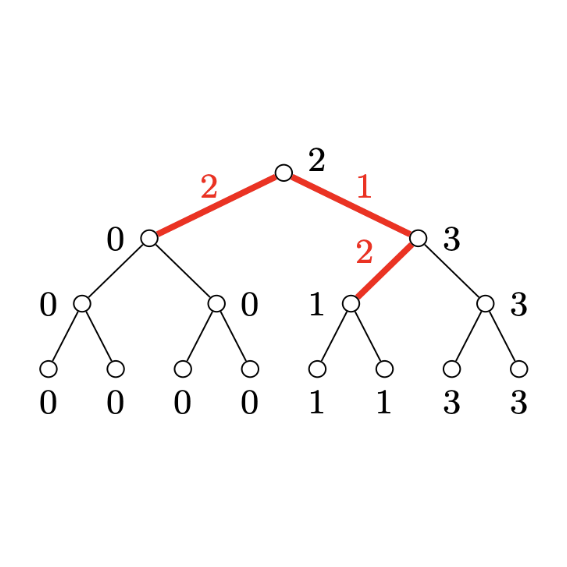
Pallavi Jain and Rohit Vaish AAAI 2024 Conference paper / arXiv Finding a many-to-one matching that maximizes Nash social welfare. |
 |
Hadi Hosseini, Andrew McGregor, Rik Sengupta, Rohit Vaish, and Vignesh Viswanathan AAMAS 2024 Conference paper / arXiv Approximation algorithms for the graphical house allocation studied in the AAMAS 2023 paper. Also, Ramanujan graphs and a cool connection between graph cuts and bitstrings. |
 |
Umang Bhaskar, Neeldhara Misra, Aditi Sethia, and Rohit Vaish SAGT 2023 Conference paper / arXiv How much welfare loss does fairness impose? The paper looks at a worst-case quantification called price of fairness for the class of generalized mean welfare measures and provides fine-grained bounds in terms of the number of agent types. |
 |
Hadi Hosseini, Joshua Kavner, Sujoy Sikdar, Rohit Vaish, and Lirong Xia arXiv Do real-world users consider approximately envy-free allocations fair? |
 |
Telikepalli Kavitha and Rohit Vaish The paper studies the best-of-both-worlds framework for fair allocations of indivisible goods, and constructs randomized allocations that are ex-ante approximately proportional and simultaneously satisfy envy-based and fair share-based ex-post guarantees. |
 |
Anjali Gupta, Shreyans J Nagori, Abhijnan Chakraborty, Rohit Vaish, Sayan Ranu, Prajit Prashant Nadkarni, Narendra Varma Dasararaju, and Muthusamy Chelliah WWW 2023 Conference paper / arXiv Fair division under two-sided cardinality constraints. |
 |
Hadi Hosseini, Justin Payan, Rik Sengupta, Rohit Vaish, and Vignesh Viswanathan AAMAS 2023 (superseded by journal version at Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems) Conference paper / arXiv How to assign a set of numbers to the vertices of a graph to minimize the sum of absolute differences along the edges? |
 |
Hadi Hosseini, Sujoy Sikdar, Rohit Vaish, and Lirong Xia AAMAS 2023 Conference paper / arXiv When agents have lexicographic preferences over mixtures of indivisible goods and chores, an EFX allocation could fail to exist. |
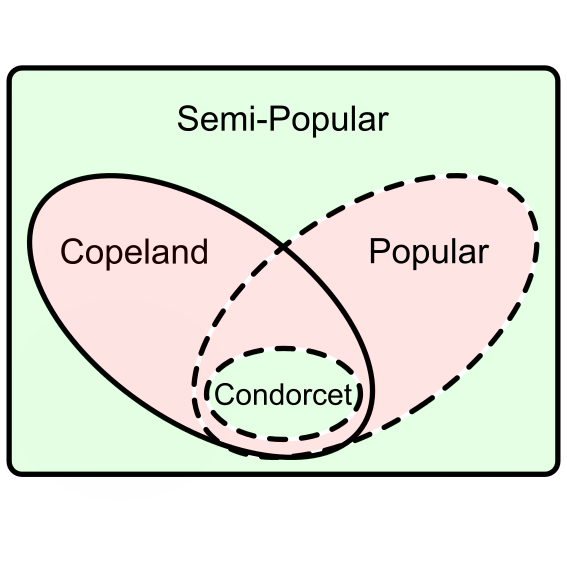 |
Telikepalli Kavitha and Rohit Vaish AAMAS 2023 Conference paper / arXiv The paper applies voting theory to the study of matchings-under-preferences, and proposes a relaxation of popularity called weak Copeland matching that is guaranteed to exist in general roommates instances with weak preferences and admits an FPRAS. |
 |
Haris Aziz, Rupert Freeman, Nisarg Shah, and Rohit Vaish Operations Research Journal paper (combines the EC 2020 paper by Freeman, Shah, and Vaish and the WINE 2020 paper by Aziz) A polynomial-time algorithm for finding a distribution over EF1 allocations that is envy-free in expectation. |
 |
Hadi Hosseini, Fatima Umar, and Rohit Vaish IJCAI 2022 Conference paper / arXiv The paper gives a polynomial-time algorithm for computing the optimal joint strategy for a man-woman pair who want to help the woman under the deferred acceptance algorithm. |
 |
Chinmay Sonar, Neeldhara Misra, P R Vaidyanathan, and Rohit Vaish COMSOC 2021 arXiv This paper gives an algorithm that, given an arrangement of indivisible items on a path and any ordering of agents, computes an EQ1 allocation consistent with the given ordering in which agents receive connected bundles and with the highest egalitarian welfare. |
 |
Farhad Mohsin, Lei Luo, Wufei Ma, Inwon Kang, Zhibing Zhao, Ao Liu, Rohit Vaish, and Lirong Xia COMSOC 2021 Workshop paper How to make group decisions when agents' preferences are specified not as rankings or numerical utilities but in natural language. |
 |
Umang Bhaskar, A R Sricharan, and Rohit Vaish APPROX 2021 Conference paper / arXiv / Video (17 min) from GAIW 2021 Resolving arbitrary envy cycles could fail to achieve EF1 even for additive chores. The paper proposes the top-trading envy cycle algorithm that guarantees EF1 for monotone chores. |
 |
Hadi Hosseini, Fatima Umar, and Rohit Vaish IJCAI 2021 Conference paper / arXiv / Video (5 min) on IITD CSE Channel Under the deferred acceptance algorithm, an agent on the proposed-to side is typically better off asking a proposer (a.k.a., an accomplice) to manipulate on her behalf rather than manipulating on her own. |
 |
Hadi Hosseini, Sujoy Sikdar, Rohit Vaish, and Lirong Xia AAAI 2021 Conference paper / arXiv Characterizing allocations that are envy-free up to any good (EFX) and Pareto optimal (PO) under lexicographic preferences. |
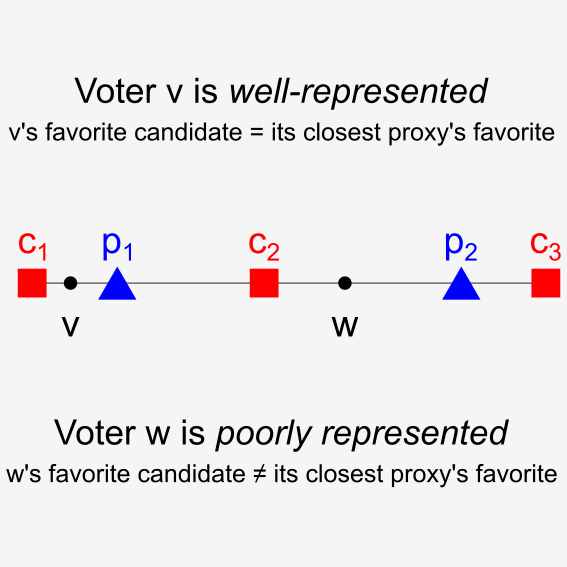 |
Elliot Anshelevich, Zack Fitzsimmons, Rohit Vaish, and Lirong Xia AAAI 2021 Conference paper / arXiv / Video (18 min) from AAAI 2021 Computing proxy arrangements that fairly represent a continuum of voters in a one-dimensional setting. |
 |
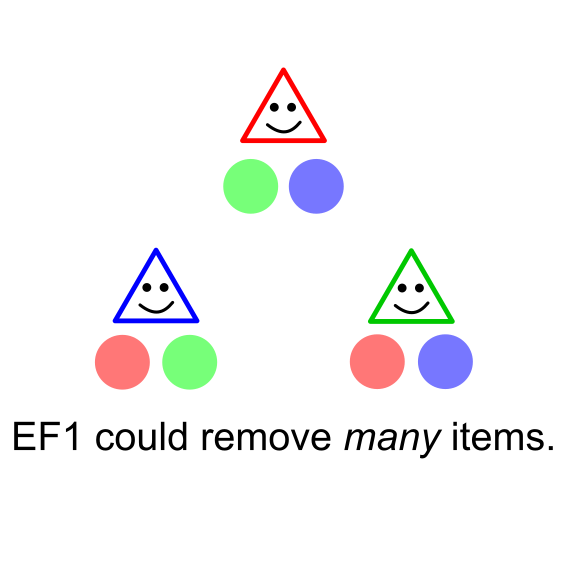
Rupert Freeman, Nisarg Shah, and Rohit Vaish EC 2020 (superseded by journal version at Operations Research) Conference paper / arXiv A polynomial-time algorithm for finding a distribution over EF1 allocations that is envy-free in expectation. |
 |
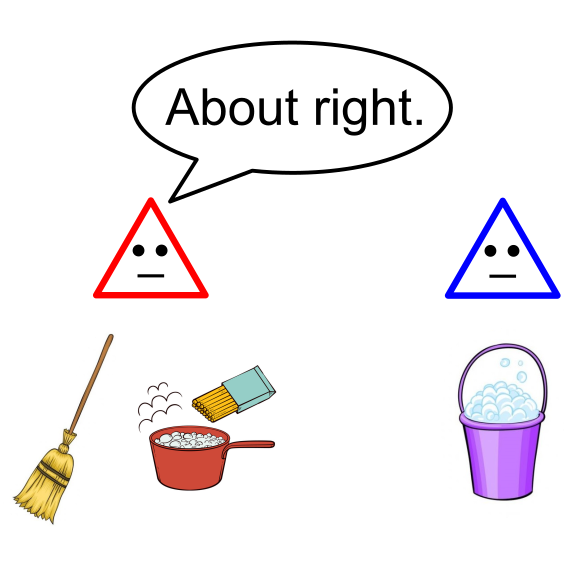
Hadi Hosseini, Sujoy Sikdar, Rohit Vaish, and Lirong Xia AAAI 2020 Conference paper / arXiv What is the smallest number of goods that need to be concealed in order to achieve envy-freeness? |
 |
Rupert Freeman, Sujoy Sikdar, Rohit Vaish, and Lirong Xia AAMAS 2020 Conference paper / arXiv A pseudopolynomial-time algorithm for finding an allocation that is equitable up to one chore (EQ1) and Pareto optimal (PO). |
 |
Ioannis Caragiannis, Aris Filos-Ratsikas, Panagiotis Kanellopoulos, and Rohit Vaish EC 2019 and Artificial Intelligence Conference paper / Journal paper / arXiv / Video (14 min) from EC 2019 / Video (30 mins) from COMSOC video seminar The paper studies computational aspects of the stable matching problem when agents have cardinal preferences and one seeks a fractional solution with high social welfare. |
 |
Rupert Freeman, Sujoy Sikdar, Rohit Vaish, and Lirong Xia IJCAI 2019 Conference paper / arXiv This paper studies approximately equitable and economically efficient allocations of indivisible goods. |
 |
Haoming Li, Sujoy Sikdar, Rohit Vaish, Junming Wang, Lirong Xia, and Chaonan Ye IJCAI 2019 Conference paper / arXiv The paper develops a framework for optimizing the time it takes a user to transform a given ranking into a desired ranking via drag-and-drop operations. |
 |
Siddharth Barman, Sanath Kumar Krishnamurthy, and Rohit Vaish AAMAS 2018 (Best Paper Nomination) Conference paper / arXiv A polynomial-time algorithm for maximizing Nash social welfare under binary valuations. |
 |
Siddharth Barman, Sanath Kumar Krishnamurthy, and Rohit Vaish EC 2018 Conference paper / arXiv An algorithmic framework for finding an allocation that is envy-free up to one good (EF1) and Pareto optimal (PO), and a 1.45-approximation algorithm for Nash social welfare. |
 |
Avrim Blum, Ioannis Caragiannis, Nika Haghtalab, Ariel Procaccia, Eviatar Procaccia, and Rohit Vaish SODA 2017 Conference paper / arXiv The paper studies a semi-random model for kidney exchange with a worst-case compatibility graph and a uniformly random assignment of patient-donor pairs to hospitals. |
 |
Rohit Vaish and Dinesh Garg IJCAI 2017 Conference paper Under the deferred acceptance algorithm, optimal manipulation by an agent on the proposed-to side is inconspicuous and stability-preserving. |
 |
Aritra Chatterjee, Ganesh Ghalme, Shweta Jain, Rohit Vaish, and Yadati Narahari UAI 2017 Conference paper Analyzing the Thomson sampling algorithm for stochastic multiarmed bandits when not all arms are available in each round. |
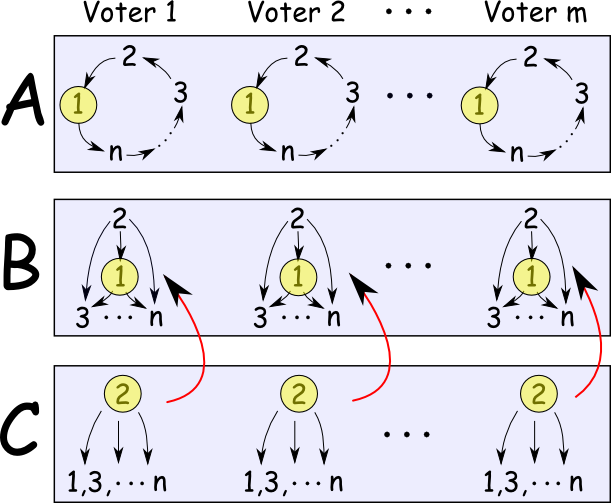 |
Rohit Vaish, Neeldhara Misra, Shivani Agarwal, and Avrim Blum AAMAS 2016 Conference paper / Full version In elections where each voter's preferences are given by a set of pairwise comparisons, no "reasonable" voting rule can prevent tactical voting, but NP-hardness comes to the rescue. |
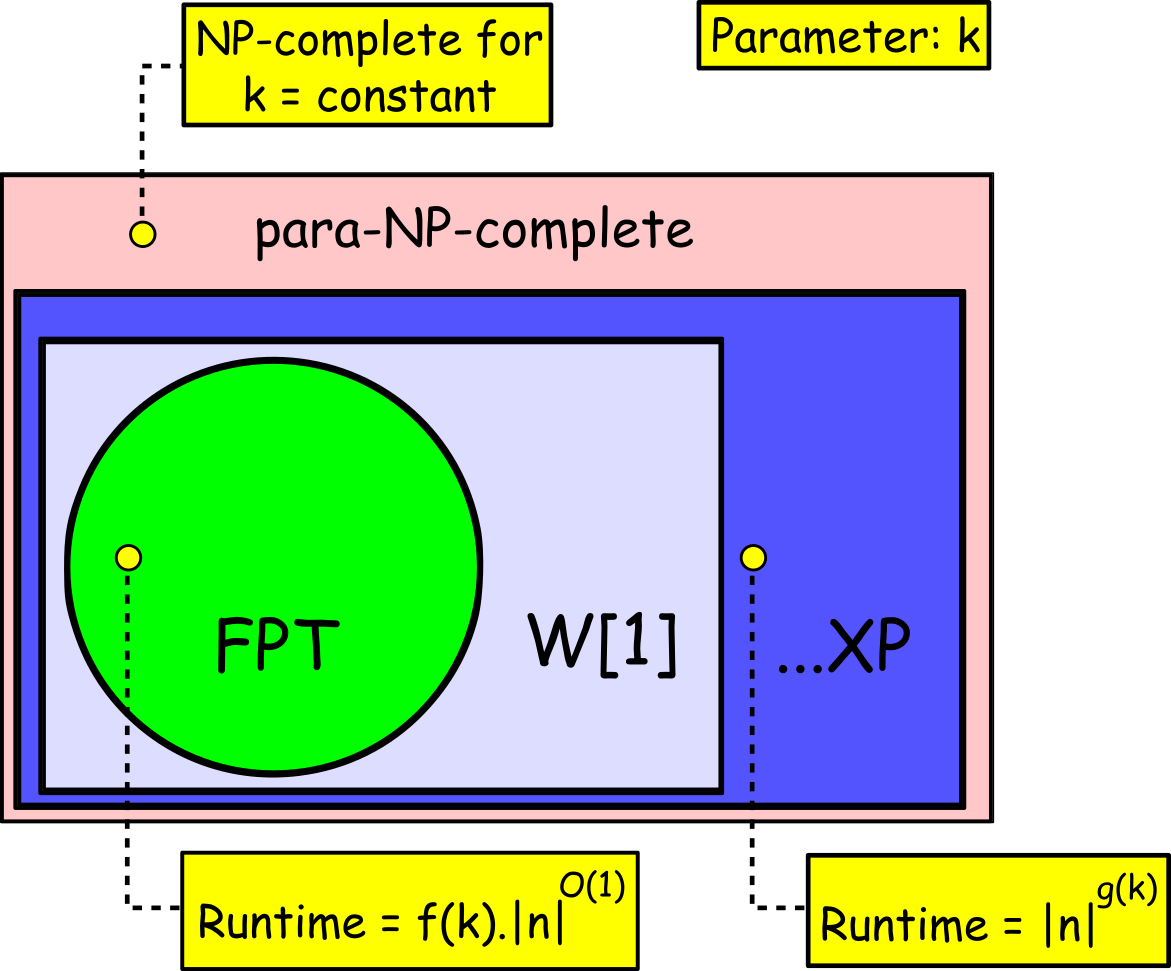 |
Rohit Vaish and Neeldhara Misra EXPLORE 2016 Workshop paper This paper undertakes a parameterized complexity analysis of the manipulation problem studied in our AAMAS 2016 paper. |
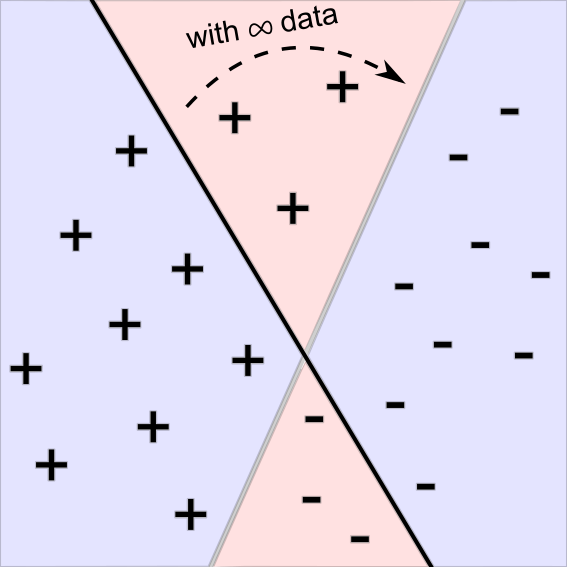 |
Harikrishna Narasimhan, Rohit Vaish, and Shivani Agarwal NeurIPS 2014 Conference paper The paper shows that plug-in algorithms are statistically consistent for non-decomposable performance measures (e.g., F-measure). |